As an ISO 9001:2015 accredited company, PT. Sinergi Industri Prima (SIP) is dedicated to providing consistent quality in our stud bolts and related services.
We consistently ensure that our specialty stud bolts meet customer and regulatory requirements by adhering to this international quality management system (QMS) standard.
This commitment to excellence guarantees that our stud bolts deliver reliable and durable performance for your critical applications in the field.
What Are Stud Bolts?
Stud bolts (or studs) are specialized fasteners that provide solid and reliable connections in various industries, including oil and gas, energy, and aerospace. Depending on the type, these versatile fasteners are characterized by their lack of heads and threaded ends or entire length. They are crucial in securing flanges and other mating surfaces in numerous applications, such as pipelines, engines, turbines, and heavy machinery.
Stud Bolt Types: Bolt Threads & Bolt Ends
Studs come in various types, each designed for specific applications and requirements. This section will explore three main categories of stud bolts: A) Threaded-end, B) Tap-End, and C) Double-End stud bolts.
Fully Threaded
As the name suggests, a fully threaded stud bolt would be threaded throughout its entire length. This design provides greater flexibility in grip length, making them suitable for applications with varying thicknesses or where precise clamping force is required. Fully threaded stud bolts are commonly used in machinery, oil and gas, automotive, and construction applications.
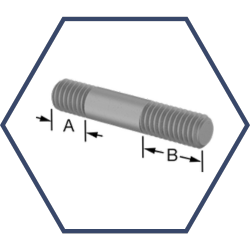
Tap-End
Tap-end stud bolts feature threads on one end and a chamfered, unthreaded tap-end on the other. The threaded end secures the bolt with a nut, while the tap-end is inserted into a pre-drilled and threaded hole in the mating component. This design allows for precise alignment and secure clamping, making tap-end stud bolts suitable for applications requiring high levels of accuracy, such as engine components and high-precision machinery.
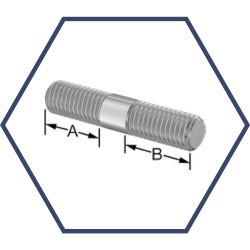
Double-End
Double-end stud bolts, or double-headed or double-end studs, have threads on both ends and an unthreaded shank in the middle. These bolts are designed for securing components with through-holes by using nuts on both ends.
The unthreaded shank provides precise alignment between the mating surfaces, while the threaded ends ensure a secure connection. Double-end studs are commonly used in flange connections, pipelines, engines, turbines, and other heavy machinery applications.
Materials Used For Stud Bolts
The choice of material for stud bolts plays a significant role in determining their performance, durability, and resistance to various environmental conditions. Five common materials used to manufacture stud bolts include carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, superalloys, and exotic materials such as Inconel and Monel.
Carbon steel
Carbon steel is popular for stud bolts due to its strength, affordability, and availability. It is an iron-based alloy with a small carbon percentage, giving it excellent tensile strength and durability.
Carbon steel studs are often used in applications where high strength and resistance to wear are required, such as heavy machinery, construction, and automotive industries. However, carbon steel is susceptible to corrosion, so that it may require additional coatings or treatments for protection in corrosive environments.
Stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, chromium, and other elements with excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. The chromium content in stainless steel forms a passive layer of chromium oxide on the surface, which protects the material from corrosion.
A stainless steel stud would be commonly used in applications where corrosion resistance is a primary concern, such as chemical plants, marine environments, and food processing facilities.
Alloy steel
Alloy steel has been modified by adding various elements, such as chromium, molybdenum, nickel, and others, to improve its mechanical properties. These alloying elements enhance the steel’s strength, hardness, toughness, and resistance to wear, making alloy steel stud bolts suitable for high-stress applications and extreme conditions. Alloy steel stud bolts are often found in the oil and gas, aerospace, and power generation industries.
Superalloy
Superalloys are high-performance materials known for their excellent mechanical strength, resistance to thermal creep deformation, and ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments. These alloys typically combine nickel, cobalt, iron, and other elements, offering exceptional performance under extreme conditions.
Superalloy stud bolts are often used in applications where conventional materials, such as aerospace, power generation, and high-temperature chemical processing industries, may not perform well. Superalloys ensure that stud bolts maintain their strength, stability, and resistance to corrosion even under the most demanding conditions.
Exotic materials (Inconel, Monel, etc.)
Exotic materials like Inconel and Monel are high-performance alloys with exceptional corrosion, heat, and pressure resistance. These materials are often used in stud bolts for specialized applications that demand superior performance in harsh environments.
Inconel is a nickel-based alloy known for its excellent resistance to high temperatures, oxidation, and corrosion, making it ideal for use in the aerospace, nuclear, and chemical processing industries.
Monel, a nickel-copper alloy, offers excellent corrosion resistance, especially in seawater and acidic environments, making it suitable for marine and chemical industries.
When selecting a material for your stud bolts, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your application, such as the expected loads, environmental conditions, and potential exposure to corrosive substances. Choosing the appropriate material ensures that your stud bolts perform optimally and provide a reliable connection.
Specifications And Standards
Stud specifications and standards ensure these fasteners’ quality, performance, and compatibility across various industries. By adhering to established standards, manufacturers can guarantee that their stud bolts meet the required mechanical properties and dimensional tolerances.
ASTM And ASME Standards
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) are leading organizations that develop and maintain standards for materials, products, and systems, including stud bolts.
ASTM and ASME standards cover many aspects, such as material composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, and manufacturing processes. Diameter, length, and thread pitch are key dimensions that affect the compatibility and performance of stud bolts in various connections.
By following these standards, manufacturers can ensure that their stud bolts are of the highest quality and suitable for the intended applications. Some common ASTM and ASME standards for stud bolts include ASTM A193, ASTM A320, and ASME B18.31.3.
Metric And Imperial Measurements
Stud bolts are available in metric and imperial measurements to cater to industries and markets worldwide. Metric sizes are based on the International System of Units (SI), and imperial measurements follow the United States customary system.
When selecting a stud, it is essential to choose the appropriate measurement system based on the requirements of your application and the standards followed in your region.
Common Grades And Coatings
Stud bolts come in various grades, which indicate their mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. Some common grades for stud bolts include B7, B8, B8M, L7, and L43. The choice of grade depends on the specific requirements of your application, such as the expected loads and environmental conditions.
In addition to grades, studs can feature various coatings to enhance their performance, appearance, and resistance to corrosion. Common coatings include zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, and PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) coatings. The choice of the coating depends on factors such as the application, environmental conditions, and the desired level of corrosion protection.
Applications Of Stud Bolts
A stud is a versatile fastener used across various industries and flange-type (e.g., weld neck, slip-on, and blind). Their ability to provide robust, secure, and precise connections makes them essential in multiple sectors.
Oil And Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, stud bolts are critical in ensuring safe and efficient operation of equipment and facilities. They commonly connect flanges, pipelines, valves, and other components, forming leak-proof seals that withstand high pressures and temperatures. The use of the appropriate stud bolts, in terms of material and grade, is essential in this industry, given the extreme conditions and potential exposure to corrosive substances.
Automotive Industry
Stud bolts have a variety of applications in the automotive industry, where they are used to assemble engines, transmissions, suspensions, and other components. They offer precise alignment and secure connections, crucial for vehicles’ proper functioning and performance. Stud bolts are often made from high-strength materials, such as alloy steel or stainless steel, to ensure durability and resistance to wear and tear.
Construction And Infrastructure
In the construction and infrastructure sector, stud bolts are used to join a number of structural components, such as steel beams, columns, and concrete slabs. They provide solid and reliable connections, which are essential for the stability and integrity of buildings, bridges, and other structures. Stud bolts used in this industry may be subjected to significant loads, requiring high-strength materials and adherence to strict standards and specifications.
Machinery And Equipment
Stud bolts are widely used in the assembly of machinery and equipment across various industries, such as manufacturing, mining, and agriculture. They help secure components together, ensuring the proper functioning and safety of the equipment. In these applications, stud bolts may be exposed to vibrations, high loads, and harsh operating conditions, necessitating durable materials and appropriate grades.
Proper Installation And Maintenance
Ensuring proper installation and maintenance of stud bolts is crucial for maintaining the integrity, safety, and efficiency of the connections they secure. Critical aspects of stud bolt installation and maintenance include correct torque application, the importance of lubrication, and inspection and replacement guidelines.
Correct Torque Application
Applying the correct torque is essential when installing a stud. Insufficient torque can lead to loose connections, while excessive torque may cause bolt deformation or failure. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations and industry standards for torque values and tightening procedures is essential. A calibrated torque wrench should ensure accurate and consistent torque application.
Importance Of Lubrication
Lubrication is critical in reducing friction between the stud bolt and nut threads, allowing for a more accurate and even distribution of the applied torque. Lubricants also help protect the threads from corrosion and galling. Before installation, applying the recommended lubricant to the threads is essential, ensuring that they are clean and free of contaminants. Some common lubricants used for stud bolts include anti-seize compounds, molybdenum disulfide-based greases, and PTFE-based lubricants.
Inspection And Replacement Guidelines
Regular inspection of stud bolts is necessary to ensure their continued performance and safety. Factors to consider during an assessment include visual signs of corrosion, wear, or damage to the threads and any evidence of loosening or movement in the connection. Industry-specific guidelines and best practices should be followed when determining the frequency and scope of inspections.
Nuts: Complementary Components
Nuts are essential components that work in conjunction with stud bolts to create secure and stable connections. By threading onto the ends of the stud bolt, nuts provide the clamping force required to hold flanges, components, or assemblies together. Available in various sizes, materials, and grades, nuts must be compatible with the stud bolts used to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
As you consider using stud bolts for your projects, here are answers to some commonly asked questions:
Why Are Stud Bolts Called A Stud?
Stud bolts are called “studs” because they are a type of fastener that does not have a head. They consist of a threaded rod with threads on both ends, designed to be secured with nuts, providing a strong and stable connection.
How Do I Choose The Right Material For A Stud Bolt?
To choose the right material for a stud bolt:
- Consider the specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and relevant industry standards.
- Compare the properties of various materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel.
- Consult with experts or suppliers like PT. Sinergi Industri Prima (SIP) for guidance, if needed.
What Are The Common Standards And Specifications For Stud Bolts?
Common standards and specifications for stud bolts include ASTM and ASME standards, which cover material grades, dimensions, and mechanical properties. These standards ensure that stud bolts comply with established application and industry guidelines.
Request a Quote
At PT. Sinergi Industri Prima (SIP), we are committed to providing high-quality, ISO 9001:2015 accredited stud bolts and fasteners that meet the most stringent industry standards.
Our team of experts is here to assist you in finding the perfect stud bolt for your application. Contact us today to explore our extensive range of specialty bolts and fasteners, and let us help you secure the success of your project.
